The History of Microwaves
The Invention of the Microwave Oven
Percy Spencer’s Discovery
In the mid-20th century, Percy Spencer, an engineer at Raytheon, stumbled upon a groundbreaking discovery. While working on radar technology, he noticed that a chocolate bar in his pocket had melted. Intrigued, he conducted further experiments, eventually leading to the invention of the microwave oven. This serendipitous moment changed the way we cook and heat food forever.
Early Commercial Models
The first commercial microwave ovens were introduced in the late 1940s. They were large, expensive, and primarily used in commercial kitchens. Over time, advancements in technology made them more affordable and compact, paving the way for household use.
Evolution of Microwave Technology
Technological Advancements
From the bulky machines of the 1940s to the sleek, multifunctional appliances of today, microwave technology has come a long way. Innovations like inverter technology and sensor cooking have made microwaves more efficient and user-friendly.
Popularity in Households
By the 1980s, microwaves had become a staple in many homes. Their convenience and versatility made them indispensable for quick meals and reheating leftovers.
Basic Principles of Microwave Operation
Electromagnetic Waves
Definition and Properties
Microwaves are a type of electromagnetic wave, similar to radio waves but with a shorter wavelength. They fall within the frequency range of 300 MHz to 300 GHz.
Frequency and Wavelength
The frequency of microwaves used in ovens is typically around 2.45 GHz. This frequency is ideal for heating food because it efficiently interacts with water molecules.
Microwave Radiation
How Microwaves Generate Heat
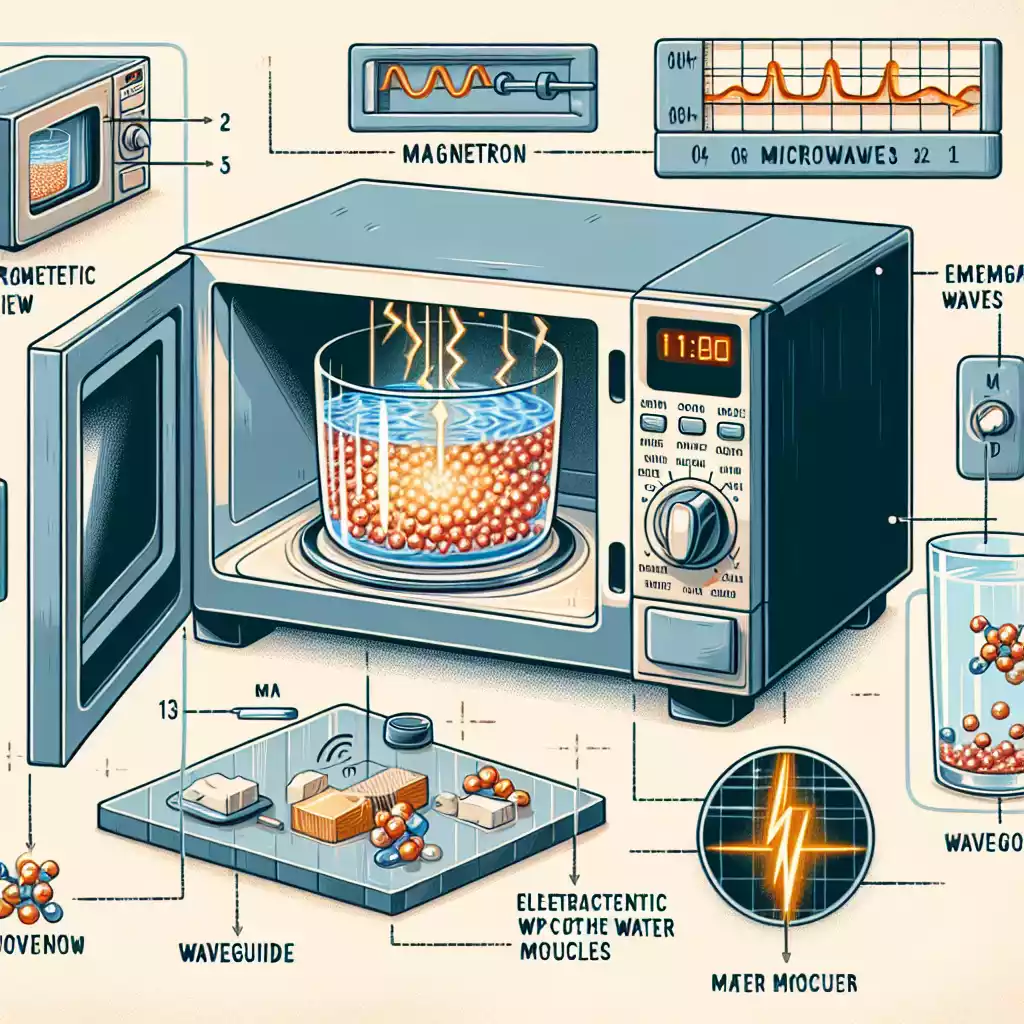
Microwaves heat food by causing water molecules to vibrate rapidly. This vibration generates heat, which cooks the food from the inside out. It’s a process known as dielectric heating.
Interaction with Water Molecules
Water molecules are polar, meaning they have a positive and negative end. When exposed to microwaves, these molecules align with the alternating electric field, creating friction and, consequently, heat.
Components of a Microwave Oven
Magnetron
Function and Structure
The magnetron is the heart of the microwave oven. It converts electrical energy into microwave radiation. This device consists of a vacuum tube and a magnetic field, which generate the microwaves.
Generation of Microwaves
Electrons emitted from the cathode spiral in the magnetic field, producing microwaves. These waves are then directed into the cooking chamber.
Waveguide
Directing Microwaves
The waveguide channels the microwaves from the magnetron to the cooking chamber. It ensures that the waves are evenly distributed for uniform heating.
Ensuring Uniform Heating
By guiding the microwaves efficiently, the waveguide helps prevent hotspots and ensures that food is cooked evenly.
Turntable
Importance of Rotation
The turntable rotates the food, ensuring that it is exposed to microwaves from all angles. This rotation helps in achieving even cooking.
Consistent Heating
Without a turntable, microwaves might only heat certain areas of the food, leading to uneven cooking. The turntable solves this problem by constantly moving the food.
How Microwaves Cook Food
Penetration Depth
Factors Affecting Penetration
The depth to which microwaves penetrate food depends on factors like the food’s density, moisture content, and composition. Generally, microwaves penetrate about 1-1.5 inches into the food.
Heating Patterns
Microwaves heat food from the outside in. The outer layers absorb most of the energy, while the inner layers cook through conduction.
Moisture Content
Impact on Cooking Efficiency
Foods with higher moisture content cook more efficiently in a microwave. The water molecules absorb the microwaves, generating heat and cooking the food.
Retention of Nutrients
Microwaving can help retain more nutrients compared to other cooking methods. The shorter cooking time and lower temperatures preserve vitamins and minerals.
Safety Mechanisms in Microwaves
Door Interlock System
Preventing Radiation Leakage
Microwave ovens are equipped with a door interlock system that prevents the oven from operating when the door is open. This mechanism ensures that no radiation leaks out.
Safety Standards
Manufacturers adhere to strict safety standards to ensure that microwaves are safe for home use. These standards regulate radiation levels and ensure proper shielding.
Shielding
Metal Mesh Screen
The door of a microwave oven has a metal mesh screen that prevents microwaves from escaping. The small holes in the mesh allow light to pass through but block the microwaves.
Faraday Cage Principle
Microwave ovens function as a Faraday cage, a structure that blocks electromagnetic fields. This principle ensures that microwaves stay inside the cooking chamber.
Common Uses of Microwaves
Cooking and Reheating
Popular Microwave Recipes
Microwaves are perfect for quick and easy recipes. From popcorn to mug cakes, the possibilities are endless. They can also cook vegetables, rice, and even pasta.
Reheating Leftovers
Reheating leftovers is one of the most common uses of microwaves. They quickly bring food back to the right temperature without drying it out.
Defrosting
Defrosting Techniques
Microwaves offer defrost settings that thaw frozen food evenly. This feature saves time compared to traditional methods like leaving food in the refrigerator.
Avoiding Uneven Thawing
To avoid uneven thawing, it’s essential to use the defrost setting and periodically check the food. Rotating and flipping the food can also help.
Advanced Features in Modern Microwaves
Inverter Technology
Precise Power Control
Inverter technology allows microwaves to deliver consistent power levels, preventing overcooking. Traditional microwaves cycle between full power and no power, while inverters maintain a steady output.
Benefits Over Traditional Models
Inverter microwaves cook food more evenly and efficiently. They are particularly useful for delicate foods that require precise temperature control.
Sensor Cooking
Automatic Adjustments
Sensor cooking technology detects the moisture and temperature of the food, adjusting the cooking time and power level automatically. This feature ensures perfect results every time.
Enhancing Cooking Experience
With sensor cooking, there’s no need to guess the cooking time. The microwave does the work for you, making the cooking process more convenient and foolproof.
Energy Efficiency of Microwaves
Power Consumption
Comparing with Other Appliances
Microwaves are more energy-efficient than conventional ovens and stovetops. They use less electricity and cook food faster, saving both time and energy.
Tips for Efficient Use
To maximize efficiency, use microwave-safe containers, cover food to retain moisture, and avoid overcooking. These practices help reduce energy consumption.
Environmental Impact
Reducing Carbon Footprint
By using less energy, microwaves contribute to a lower carbon footprint. They are an eco-friendly option for cooking and reheating food.
Sustainable Practices
Choosing energy-efficient models and using them wisely can further enhance their environmental benefits. Regular maintenance also ensures optimal performance.
Maintenance and Care for Microwaves
Cleaning Tips
Regular Maintenance
Keeping your microwave clean is essential for its longevity. Wipe down the interior after each use and deep clean it weekly to prevent buildup.
Removing Odors
To remove odors, place a bowl of water with lemon slices inside the microwave and heat it for a few minutes. The steam will loosen grime, making it easier to clean.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Identifying Problems
Common issues include the microwave not heating, strange noises, or the turntable not rotating. Identifying these problems early can prevent more significant issues.
Simple Fixes
Many issues can be resolved with simple fixes, like resetting the microwave, checking the power source, or cleaning the door seals. If problems persist, consult the manual or a professional.
Myths and Misconceptions about Microwaves
Microwave Radiation Myths
Debunking Health Risks
Contrary to popular belief, microwaves do not cause cancer. They use non-ionizing radiation, which is not harmful to human health.
Scientific Evidence
Numerous studies have shown that microwave ovens are safe when used correctly. They do not alter the molecular structure of food in a harmful way.
Nutritional Impact
Preserving Nutrients
Microwaving can preserve more nutrients compared to boiling or frying. The shorter cooking time and lower temperatures help retain vitamins and minerals.
Comparing with Other Cooking Methods
While some nutrients may be lost during microwaving, the same is true for other cooking methods. Overall, microwaving is a healthy and efficient way to prepare food.
Future of Microwave Technology
Innovations on the Horizon
Smart Microwaves
The future of microwaves lies in smart technology. Features like Wi-Fi connectivity, voice control, and integration with smart home systems are becoming more common.
Integration with IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) will enable microwaves to communicate with other devices, making the cooking process even more seamless and automated.
Potential Developments
Improved Efficiency
Future microwaves will likely be more energy-efficient, reducing both power consumption and cooking time. This improvement will benefit both consumers and the environment.
Enhanced Safety Features
Ongoing research aims to enhance safety features, ensuring that microwaves remain a safe and reliable kitchen appliance.
FAQs about Microwaves
FAQ 1: How do microwaves heat food?
Microwaves heat food by causing water molecules to vibrate, generating heat through friction. This process cooks the food from the inside out.
FAQ 2: Are microwaves safe for cooking?
Yes, microwaves are safe for cooking when used correctly. They use non-ionizing radiation, which does not pose health risks.
FAQ 3: Can microwaves cook food evenly?
Microwaves can cook food evenly if used properly. Features like turntables and inverter technology help achieve consistent results.
FAQ 4: What materials are microwave-safe?
Materials like glass, ceramic, and certain plastics are microwave-safe. Avoid using metal containers, as they can cause sparks and damage the microwave.
FAQ 5: How can I maintain my microwave?
Regular cleaning, using microwave-safe containers, and following the manufacturer’s instructions can help maintain your microwave’s performance and longevity.
Conclusion
Understanding how microwaves work reveals their importance in modern kitchens. From the invention by Percy Spencer to today’s advanced models, microwaves have transformed cooking. By using electromagnetic waves to heat food efficiently, they offer convenience and versatility. With proper use and maintenance, microwaves continue to be a valuable appliance, making meal preparation quick and easy.