The Basics of Microwave Technology
What is a Microwave?
A microwave oven is a kitchen appliance that uses electromagnetic waves to heat and cook food. This invention revolutionized cooking in the 20th century by offering a quick and efficient way to prepare meals. Unlike traditional ovens that heat food from the outside in, microwaves penetrate food, heating it from the inside out.
History of Microwave Ovens
The journey of the microwave oven began during World War II. Percy Spencer, an engineer working with radar technology, noticed that microwaves from an active radar melted a chocolate bar in his pocket. This serendipitous discovery led to the development of the first microwave oven, called the Radarange, in 1947. Initially, these ovens were bulky and expensive, but by the 1970s, they became more affordable and compact, finding a place in households worldwide.
The Science Behind Microwaves
Electromagnetic Waves Explained
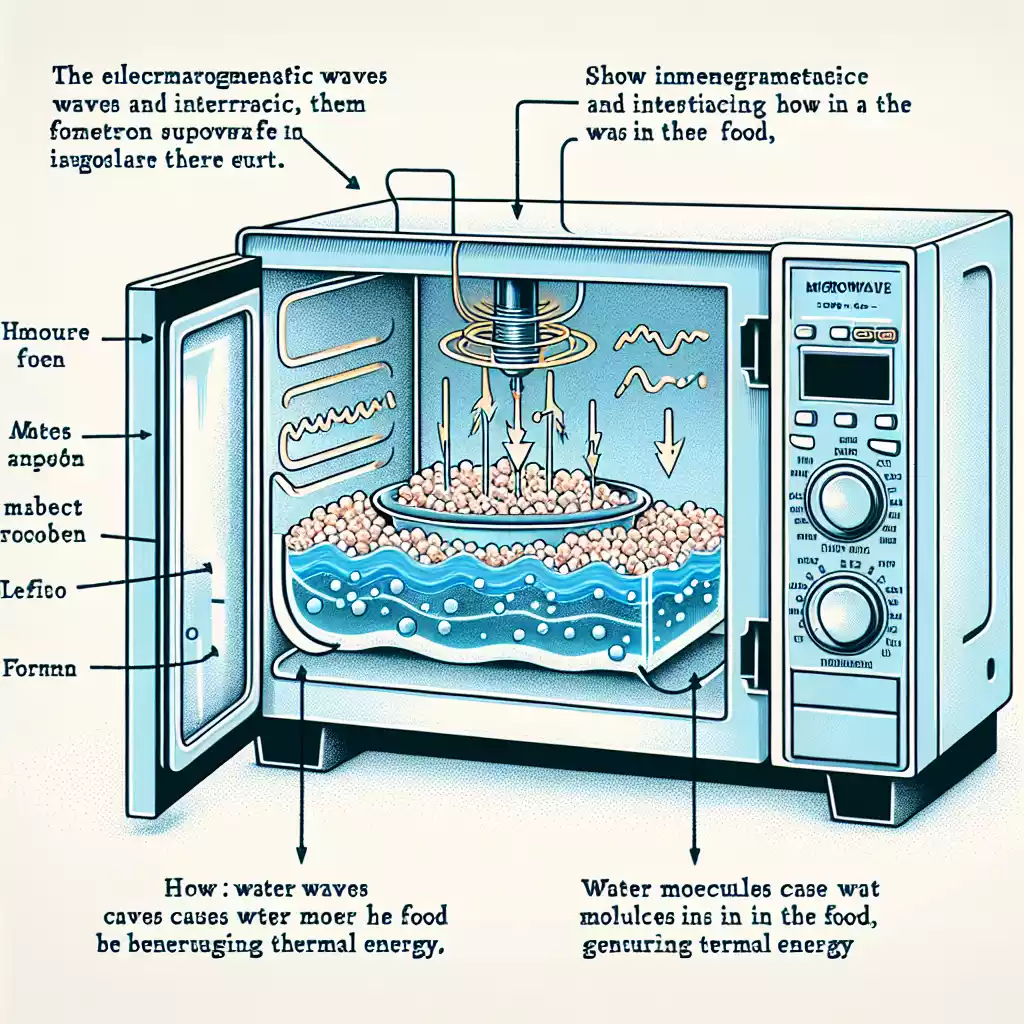
Microwaves are a type of electromagnetic wave, situated between radio waves and infrared radiation on the electromagnetic spectrum. They have wavelengths ranging from one millimeter to one meter and frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. These waves are invisible to the naked eye but are powerful enough to cause water molecules in food to vibrate, generating heat.
How Microwaves Generate Heat
Microwave ovens generate microwaves using a component called a magnetron. This device converts electrical energy into microwave radiation. When microwaves enter the food, they excite water molecules, causing them to vibrate rapidly. This vibration generates heat, which cooks the food. Because microwaves target water molecules, foods with higher water content tend to heat more quickly.
Components of a Microwave Oven

Magnetron: The Heart of the Microwave
The magnetron is the core component of a microwave oven. It generates the microwaves that cook the food. This device consists of a heated cathode that emits electrons, which are then accelerated by a magnetic field. The interaction between the electrons and the magnetic field produces microwaves.
Waveguide: Directing the Microwaves
The waveguide is a metal tube that directs microwaves from the magnetron into the cooking chamber. It ensures that microwaves are evenly distributed throughout the oven, allowing for uniform cooking. Without the waveguide, microwaves would scatter, leading to uneven heating.
How Microwaves Interact with Food
Water Molecules and Microwave Absorption
Microwaves are particularly effective at heating foods with high water content. When microwaves penetrate food, they cause water molecules to oscillate, generating heat through friction. This process, known as dielectric heating, ensures that food cooks from the inside out.
Heat Distribution in Food
One common issue with microwave cooking is uneven heating. This occurs because microwaves can only penetrate food to a certain depth, usually about one inch. Beyond this point, heat is transferred through conduction. To mitigate this, many microwaves have turntables that rotate the food, ensuring even exposure to microwaves.
Advantages of Using Microwaves for Cooking
Speed and Efficiency
Microwaves cook food significantly faster than conventional ovens. A dish that takes an hour in a traditional oven might only take 10 minutes in a microwave. This efficiency makes microwaves ideal for quick meals and reheating leftovers.
Energy Consumption
Microwave ovens are more energy-efficient than traditional ovens. They use less electricity because they cook food faster and don’t need to preheat. This makes them a cost-effective option for everyday cooking.
Common Misconceptions About Microwaves
Radiation Concerns
Many people worry about radiation from microwave ovens. However, the microwaves used in these ovens are non-ionizing, meaning they don’t have enough energy to damage DNA or cause cancer. Microwave ovens are designed with safety features, like metal shields and door interlocks, to prevent radiation from escaping.
Nutrient Loss in Food
Another misconception is that microwaves destroy nutrients in food. In reality, microwaving can preserve more nutrients compared to other cooking methods. Because microwaves cook food quickly and with less water, they minimize nutrient loss.
Practical Tips for Microwave Cooking
Choosing Microwave-Safe Containers
Not all containers are safe for microwave use. Avoid metal containers, as they can cause sparks and fires. Opt for microwave-safe glass, ceramic, or plastic containers. Look for labels indicating microwave safety, and avoid containers with metallic paint or trim.
Avoiding Uneven Heating
To ensure even heating, stir or rotate food halfway through the cooking process. Covering food with a microwave-safe lid or microwave-safe plastic wrap can also help trap steam, promoting even cooking.
Relevant Data Table
| Food Item | Microwave Power Level | Cooking Time (Minutes) | Special Instructions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frozen Vegetables | High | 5-7 | Add 1-2 tablespoons of water |
| Baked Potato | High | 10-12 | Prick with a fork, rotate halfway |
| Popcorn | High | 2-4 | Use microwave-safe popcorn bag |
| Chicken Breast | Medium-High | 8-10 | Cover with microwave-safe lid |
FAQs
FAQ 1: How do microwaves cook food so quickly?
Microwaves cook food quickly by directly heating water molecules inside the food. This process generates heat from within, reducing cooking time compared to conventional ovens that heat food from the outside in.
FAQ 2: Are microwaves safe for cooking?
Yes, microwaves are safe for cooking. They use non-ionizing radiation, which doesn’t have enough energy to damage DNA or cause cancer. Microwave ovens are equipped with safety features to prevent radiation leakage.
FAQ 3: Can microwaves destroy nutrients in food?
Microwaves can actually preserve more nutrients compared to other cooking methods. They cook food quickly and with minimal water, which helps retain vitamins and minerals.
FAQ 4: What materials are safe to use in a microwave?
Safe materials for microwave use include microwave-safe glass, ceramic, and certain plastics. Avoid metal containers and those with metallic paint or trim, as they can cause sparks and fires.
FAQ 5: Why do some foods heat unevenly in a microwave?
Uneven heating occurs because microwaves penetrate food to a certain depth, usually about one inch. Beyond this point, heat is transferred through conduction. Using a turntable and stirring food halfway can help achieve even heating.
Conclusion
Understanding how microwaves heat food involves grasping the basics of microwave technology, the science behind electromagnetic waves, and the interaction between microwaves and food. Microwave ovens offer a quick, efficient, and energy-saving method for cooking, with several advantages over traditional ovens. By choosing the right containers and following practical tips, you can maximize the benefits of microwave cooking. Remember, microwaves are safe, effective, and can even help preserve nutrients in your food.