How Microwave Oven Works
Introduction to Microwave Ovens
Microwave ovens are a staple in modern kitchens, revolutionizing how we cook and reheat food. But how did this nifty appliance come to be, and what makes it tick? Let’s take a journey back to the 1940s. During World War II, a self-taught engineer named Percy Spencer stumbled upon the microwave technology while working with radar equipment. One day, he noticed that a candy bar in his pocket had melted while he was testing a magnetron, a device that emits microwaves. This accidental discovery led to the creation of the first microwave oven, forever changing our culinary habits.
Fast forward to today, microwave ovens are ubiquitous, found in almost every household. They offer convenience, speed, and efficiency, making them indispensable. But how exactly do they work? In essence, microwave ovens use electromagnetic waves to heat food quickly. These waves excite water molecules within the food, causing them to vibrate and produce heat. This process is what allows microwave ovens to cook food so rapidly. Now, let’s dive deeper into the fascinating mechanics and features of this kitchen marvel.
Basic Principles of Microwave Ovens
Electromagnetic Waves and Microwave Radiation
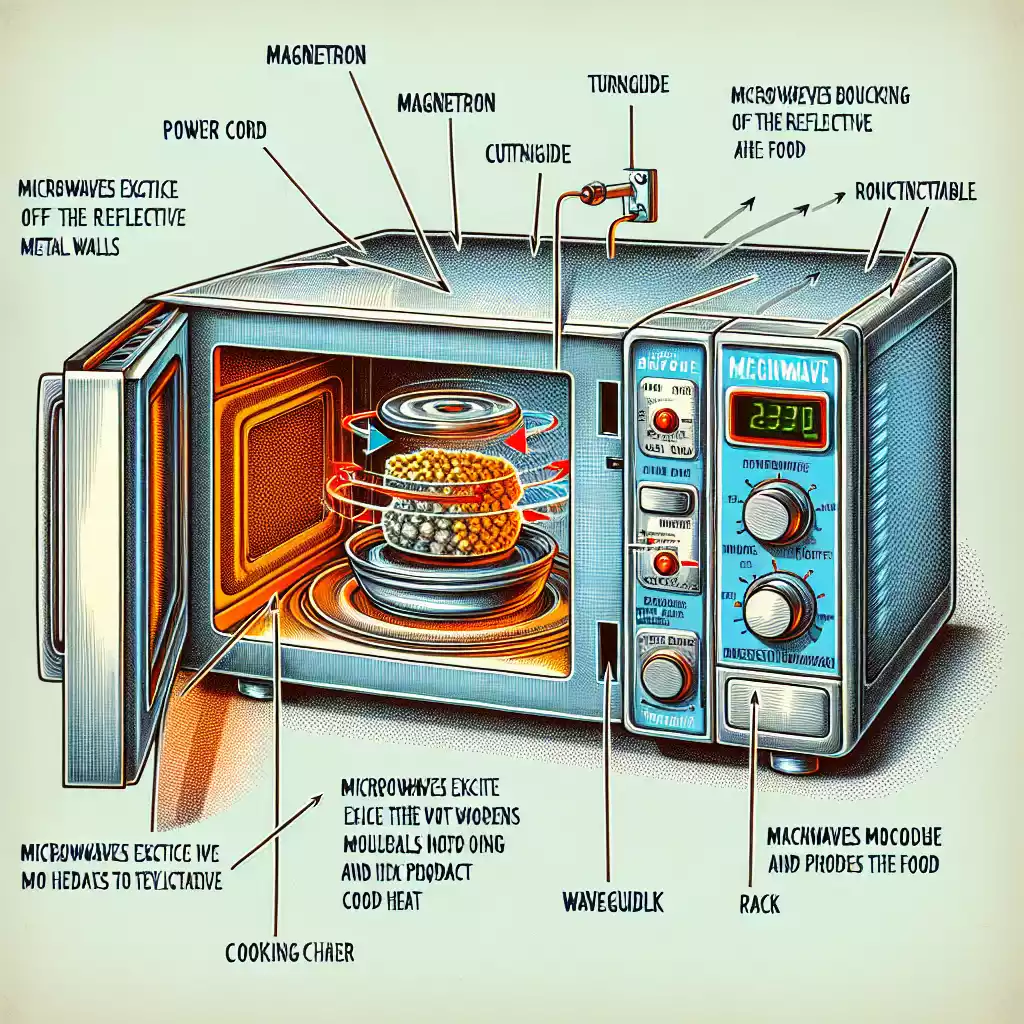
Microwave ovens operate using electromagnetic waves, specifically microwaves, which fall within the radio wave spectrum. These waves are generated by a component called the magnetron. The magnetron converts electrical energy into microwave radiation, which then penetrates the food. Unlike conventional ovens, microwaves heat food from the inside out, making the cooking process much faster.
How Microwaves Generate Heat
Microwaves target water molecules within the food. When these molecules absorb the microwave energy, they begin to vibrate rapidly, creating friction. This friction produces heat, which cooks the food. This method is highly efficient because it directly heats the food rather than the surrounding air, as in traditional ovens.
Key Components of a Microwave Oven
Magnetron: The Heart of the Microwave
The magnetron is the core component of any microwave oven. It generates the microwaves that cook the food. Invented during World War II for radar systems, the magnetron was later adapted for cooking. It consists of a cathode and an anode, surrounded by magnets. When electricity passes through the magnetron, it creates microwaves that are directed into the cooking chamber.
Waveguide: Directing Microwaves
The waveguide is a metal tube that directs the microwaves from the magnetron into the cooking chamber. It ensures that the microwaves are evenly distributed, allowing the food to cook uniformly. Without the waveguide, the microwaves would disperse randomly, leading to uneven cooking.
Turntable: Ensuring Even Cooking
Most microwave ovens come with a turntable, a rotating glass plate that sits at the bottom of the cooking chamber. The turntable rotates the food, ensuring that it is exposed to microwaves from all angles. This feature is crucial for even cooking, as it prevents hot and cold spots.
How a Microwave Oven Cooks Food
Interaction of Microwaves with Water Molecules
Microwaves primarily target water molecules, which are abundant in most foods. When these molecules absorb microwave energy, they vibrate rapidly, creating heat through friction. This process is efficient and quick, making microwave ovens ideal for cooking and reheating food.
The Role of Microwave-Safe Containers
Using the right containers is crucial when cooking with a microwave oven. Microwave-safe containers are designed to withstand the intense heat generated by microwaves. Materials like glass, ceramic, and certain plastics are safe to use. Metal containers, on the other hand, can cause sparks and should be avoided.
Safety Features in Microwave Ovens
Door Interlock Mechanism
Microwave ovens come equipped with safety features to prevent accidents. One such feature is the door interlock mechanism. This mechanism ensures that the microwave cannot operate unless the door is securely closed. It prevents harmful microwave radiation from escaping, protecting users from potential harm.
Shielding and Radiation Safety
Microwave ovens are designed with shielding to contain microwave radiation. The cooking chamber is lined with metal, which reflects microwaves back into the chamber. The door also has a metal mesh that prevents microwaves from escaping. These safety features make microwave ovens safe for everyday use.
Advanced Features in Modern Microwave Ovens
Convection and Combination Microwaves
Modern microwave ovens come with advanced features like convection and combination cooking. Convection microwaves have a built-in fan and heating element, allowing them to function as both a microwave and a convection oven. Combination microwaves offer the best of both worlds, providing the speed of microwave cooking and the browning and crisping of convection cooking.
Smart Microwaves and Connectivity
The latest innovation in microwave technology is smart microwaves. These appliances come with Wi-Fi connectivity, allowing users to control them remotely via smartphone apps. Smart microwaves also offer voice control and pre-programmed cooking settings, making them more convenient and user-friendly.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
Addressing Uneven Cooking
Uneven cooking is a common issue with microwave ovens. It can be caused by improper placement of food or using the wrong containers. To ensure even cooking, always use microwave-safe containers and place food in the center of the turntable. Stirring or rotating food halfway through the cooking process can also help.
Handling Microwave Malfunctions
Microwave ovens can sometimes malfunction. Common issues include the microwave not heating, the turntable not rotating, or strange noises. Most of these problems can be fixed by checking the power supply, ensuring the door is closed properly, or resetting the microwave. If the issue persists, it may be best to consult a professional technician.
Maintenance and Care for Microwave Ovens
Cleaning Tips and Best Practices
Regular cleaning is essential for maintaining your microwave oven. Food spills and splatters can lead to unpleasant odors and bacteria growth. To clean your microwave, use a damp cloth and mild detergent. For stubborn stains, a mixture of vinegar and water can be effective. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials that can damage the interior.
Extending the Lifespan of Your Microwave
Proper care and maintenance can extend the lifespan of your microwave oven. Avoid overloading the microwave and using it for purposes other than cooking or reheating food. Regularly check the door seal and hinges to ensure they are in good condition. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines for use and maintenance can also help.
Environmental Impact and Energy Efficiency
Energy Consumption of Microwave Ovens
Microwave ovens are more energy-efficient than traditional ovens because they cook food quickly. They use less electricity, making them an eco-friendly option for cooking and reheating food. However, the energy consumption can vary depending on the model and features of the microwave.
Eco-Friendly Microwave Options
For those looking to reduce their environmental footprint, eco-friendly microwave options are available. These models are designed to consume less energy and have features like energy-saving modes. Some manufacturers also use sustainable materials in the construction of their microwaves.
FAQs about Microwave Ovens
FAQ 1: Can I use metal in a microwave oven?
No, using metal in a microwave oven can cause sparks and potentially damage the appliance. Always use microwave-safe containers made of glass, ceramic, or certain plastics.
FAQ 2: How do I know if my microwave is leaking radiation?
Most microwave ovens have safety features to prevent radiation leakage. However, if you suspect a leak, you can use a microwave leakage detector or consult a professional technician.
FAQ 3: What foods should not be microwaved?
Certain foods, like eggs in their shells, can explode when microwaved. Other foods, like grapes and hot peppers, can cause sparks or release harmful fumes. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for safe microwave cooking.
FAQ 4: How often should I replace my microwave oven?
The lifespan of a microwave oven can vary, but most models last between 7 to 10 years. If your microwave shows signs of wear and tear or malfunctions frequently, it may be time to replace it.
FAQ 5: Are microwave ovens safe for children to use?
Microwave ovens are generally safe for children to use, provided they are supervised and follow safety guidelines. Teach children to use microwave-safe containers and avoid overheating food.
Conclusion
Microwave ovens have transformed the way we cook and reheat food, offering speed, convenience, and efficiency. From their humble beginnings in the 1940s to the advanced models of today, microwave ovens continue to evolve, incorporating new features and technologies. By understanding how they work and following proper care and safety guidelines, you can make the most of this versatile kitchen appliance.