Introduction
Microwaves have revolutionized how we prepare meals, offering a quick and convenient way to heat food. But what happens when your trusty microwave suddenly stops working? Many people wonder if their microwave has fuses and if a blown fuse might be the culprit. Fuses are essential safety components in many electrical devices, including microwaves. They protect the appliance from electrical surges and overheating, ensuring safe operation. By understanding the role of fuses in microwaves, you can diagnose and potentially fix common issues, saving time and money. Let’s explore the ins and outs of microwave fuses, their types, and how to handle them safely.
Understanding Microwave Components
The Role of Fuses in Electrical Appliances
Fuses are small but mighty components that play a crucial role in protecting electrical devices. They act as a safety barrier, preventing electrical overloads that can cause fires or damage. When the electrical current exceeds a safe level, the fuse blows, cutting off the power supply to prevent further harm. In microwaves, fuses are particularly important because they handle high voltage and intense heat.
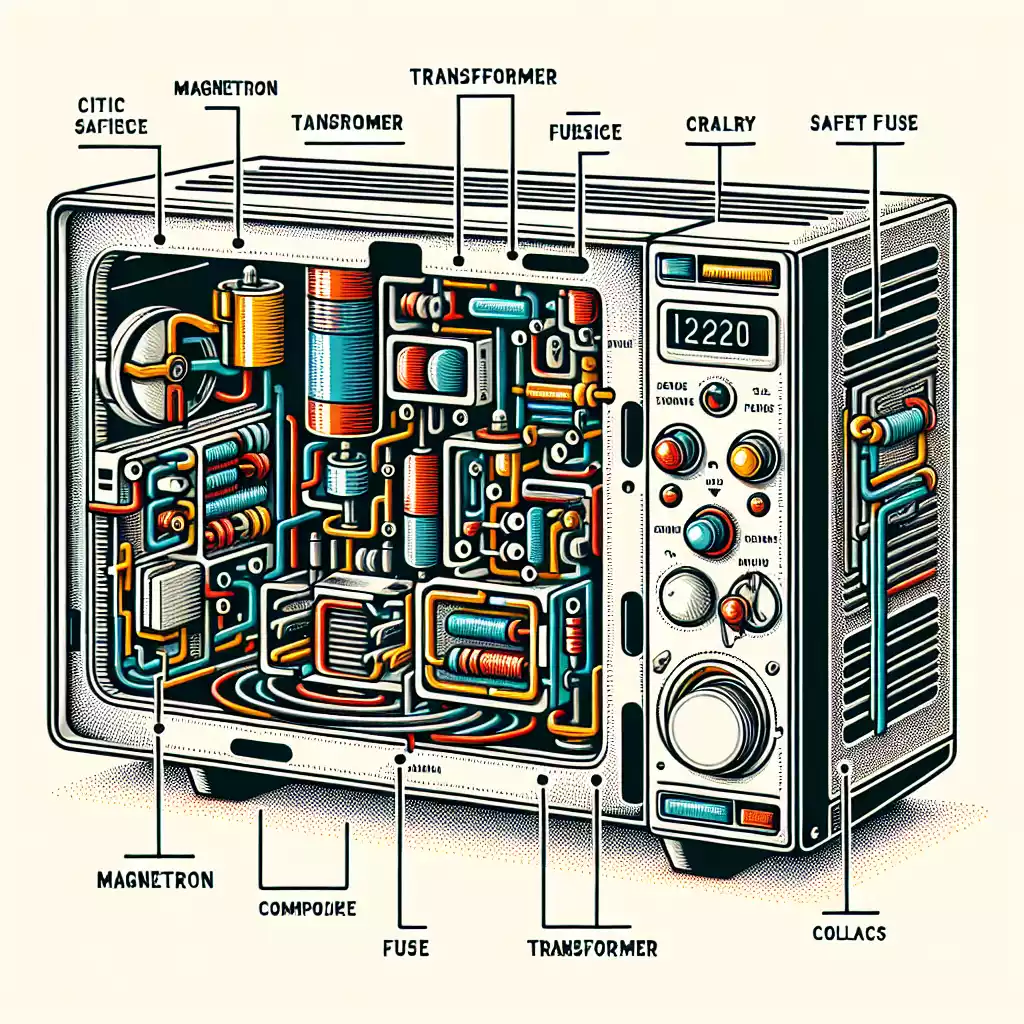
Key Components of a Microwave
To understand where fuses fit into the picture, it’s helpful to know the key components of a microwave:
• Magnetron: Generates the microwaves that cook the food.
• Transformer: Steps up the voltage to power the magnetron.
• Capacitor: Stores electrical energy.
• Diode: Converts AC to DC voltage.
• Control Panel: Allows you to set cooking times and power levels.
Types of Fuses in Microwaves
Thermal Fuses
Thermal fuses are designed to prevent overheating. They monitor the temperature inside the microwave and blow if it gets too hot. This action stops the microwave from operating, protecting it from potential damage.
Ceramic Fuses
Ceramic fuses protect against electrical surges. Unlike thermal fuses, they respond to electrical issues rather than temperature. These fuses are typically found in the power supply circuit and are crucial for safe operation.
How to Identify a Blown Fuse
Symptoms of a Blown Fuse
Identifying a blown fuse in your microwave can save you a lot of trouble. Common symptoms include:
– Microwave not turning on
– Display not working
– No response when pressing buttons
– Microwave stopping mid-cycle
Visual Inspection of Fuses
A visual inspection can often confirm a blown fuse. Here’s how to do it:
1. Unplug the Microwave: Safety first.
2. Remove the Outer Cover: Use a screwdriver to access the internal components.
3. Locate the Fuse: Check the user manual for its exact location.
4. Inspect the Fuse: Look for a broken wire or burn marks inside the fuse.
Steps to Replace a Microwave Fuse
Safety Precautions Before Starting
Replacing a fuse involves working with electrical components, so safety is paramount. Here are some precautions:
• Unplug the Microwave: Always disconnect from the power source.
• Wear Rubber Gloves: Protect yourself from electrical shocks.
• Use Insulated Tools: Ensure all tools are safe for electrical work.
Tools Needed for Fuse Replacement
Before you start, gather these tools:
– Screwdriver
– Needle-nose pliers
– Replacement fuse (specified by the manufacturer)
– Multimeter (optional, for testing)
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing a Fuse
1. Unplug the Microwave: Ensure no power is running to the appliance.
2. Remove the Outer Cover: Use a screwdriver to access the internal components.
3. Locate the Fuse: Refer to the user manual if needed.
4. Remove the Blown Fuse: Use needle-nose pliers to carefully extract the fuse.
5. Test the Fuse: Use a multimeter to confirm it’s blown.
6. Insert the New Fuse: Place the new fuse in the holder.
7. Reassemble the Microwave: Put the cover back on and secure it with screws.
8. Plug in and Test: Restore power and test the microwave.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Using Incorrect Fuse Types
Using the wrong type of fuse can cause further damage or pose a safety risk. Always use the fuse specified by the manufacturer.
Not Following Safety Guidelines
Ignoring safety guidelines can result in electrical shocks or damage to the microwave. Always follow safety precautions and use the right tools.
When to Seek Professional Help
Complex Electrical Issues
If replacing the fuse doesn’t solve the problem, you might be dealing with more complex electrical issues. In such cases, it’s best to consult a professional technician.
Warranty Considerations
If your microwave is still under warranty, attempting DIY repairs might void it. Always check warranty terms before proceeding with repairs.
Maintenance Tips to Prevent Fuse Issues
Regular Cleaning
Keeping your microwave clean can prevent many issues. Food particles and grease can cause overheating, leading to blown fuses.
Avoiding Overloads
Avoid overloading your microwave with heavy or oversized items. Overloading can strain the internal components, increasing the risk of blown fuses.
FAQs about Microwave Fuses
FAQ 1: What causes a microwave fuse to blow?
Overheating, electrical surges, or faulty components can cause a fuse to blow.
FAQ 2: Can I use any type of fuse in my microwave?
No, always use the fuse specified by the manufacturer to ensure safety and proper operation.
FAQ 3: How often should I check my microwave’s fuse?
Checking the fuse annually or when experiencing issues can help maintain your microwave’s performance.
FAQ 4: Are microwave fuses expensive?
Generally, microwave fuses are inexpensive, ranging from $1 to $10.
FAQ 5: Can a microwave work without a fuse?
No, the fuse is essential for safety and proper operation. Operating without a fuse can be dangerous.
Relevant Data Table
| Type of Fuse | Function | Common Issues |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Fuse | Prevents overheating | Tripping due to high temperature |
| Ceramic Fuse | Protects against power surges | Blowing due to electrical faults |
Conclusion
Understanding the role and function of fuses in microwaves is crucial for diagnosing and fixing common issues. By following safety guidelines and using the correct fuse type, you can ensure the longevity and safe operation of your microwave. If unsure, always seek professional help to avoid further damage or safety risks.

