Introduction
Imagine stepping into your kitchen, late for work, and needing a quick breakfast. You pop a bowl of oatmeal into a boxy machine, press a button, and within minutes, your meal is hot and ready. This marvel is the microwave oven, a staple in households around the globe. But how does it work? What makes this appliance so efficient at heating food quickly?
Microwave ovens operate using electromagnetic waves, specifically microwaves, to heat food. This technology, discovered quite by accident, has revolutionized the way we cook. The journey from a radar experiment to the kitchen countertop is as fascinating as the science behind it. This article will explore the inner workings of microwave ovens, the history of their development, practical tips for use, common misconceptions, and the various types of microwave technology available today. By the end, you’ll not only understand how microwaves work but also how to use them effectively and safely.
How Microwaves Work
The Science Behind Microwaves
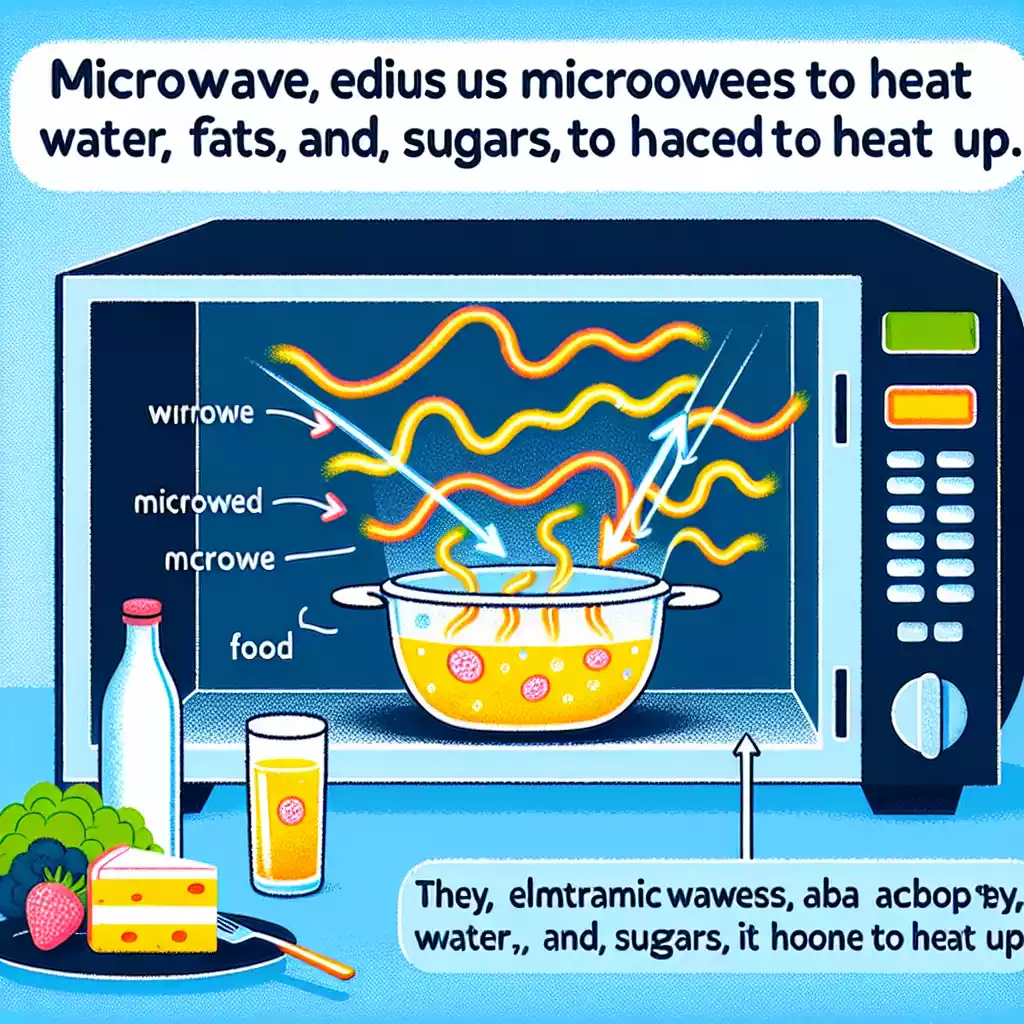
Microwaves utilize electromagnetic radiation to heat food. These waves fall between radio waves and infrared light on the electromagnetic spectrum.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is a range of all types of electromagnetic radiation. Microwaves are situated between radio waves and infrared light.
Microwave Frequency
Microwave ovens typically operate at a frequency of 2.45 GHz, which is ideal for heating water molecules in food.
Components of a Microwave Oven
A microwave oven consists of several key components that work together to heat food efficiently.
Magnetron
The magnetron generates microwaves by converting electrical energy into microwave radiation.
Waveguide
The waveguide directs the microwaves from the magnetron to the cooking chamber.
Turntable
The turntable ensures even cooking by rotating the food, allowing microwaves to penetrate from different angles.
History of Microwave Ovens

Invention of the Microwave
The microwave oven was invented accidentally by Percy Spencer while working on radar technology during World War II.
Percy Spencer’s Discovery
Spencer noticed that a chocolate bar in his pocket melted when exposed to radar waves, leading to the development of the first microwave oven.
Commercialization
The first commercial microwave oven, the Radarange, was introduced by Raytheon in 1947.
Evolution of Microwave Technology
Microwave ovens have evolved significantly since their invention, becoming more efficient and user-friendly.
Early Models
Early microwave ovens were large and expensive, making them impractical for household use.
Modern Microwaves
Today’s microwaves are compact, affordable, and feature advanced cooking modes and safety features.
Practical Tips for Using Microwaves
Cooking Tips
Using a microwave effectively requires understanding its strengths and limitations.
Even Heating
To ensure even heating, stir food halfway through the cooking process and use microwave-safe containers.
Power Levels
Adjusting the power level can help cook food more evenly and prevent overcooking.
Safety Tips
Safety is paramount when using a microwave to avoid accidents and ensure proper food handling.
Microwave-Safe Materials
Always use microwave-safe containers and avoid metal, which can cause sparks and fires.
Avoid Overheating
Overheating liquids can cause them to explode, so always monitor cooking times and use a microwave-safe cover.
Common Misconceptions About Microwaves
Microwaves and Radiation
Many people have misconceptions about the safety of microwave radiation.
Ionizing vs. Non-Ionizing Radiation
Microwaves use non-ionizing radiation, which is not harmful and does not make food radioactive.
Health Risks
There is no scientific evidence to suggest that microwaves pose significant health risks when used properly.
Nutrient Loss
Another common misconception is that microwaving food destroys its nutrients.
Nutrient Retention
Microwaving can actually preserve more nutrients compared to other cooking methods, as it cooks food quickly and with less water.
Cooking Methods Comparison
Comparing different cooking methods reveals that microwaving is one of the most efficient ways to retain nutrients in food.
Variations in Microwave Technology
Convection Microwaves
Convection microwaves combine traditional microwave technology with convection cooking, offering more versatility.
How Convection Microwaves Work
These microwaves use a fan and heating element to circulate hot air, allowing for baking and roasting.
Benefits of Convection Microwaves
Convection microwaves provide even cooking and browning, making them ideal for a wider range of recipes.
Inverter Microwaves
Inverter technology offers more precise control over cooking power and time.
How Inverter Microwaves Work
Inverter microwaves use a continuous power supply, unlike traditional microwaves that cycle on and off.
Advantages of Inverter Microwaves
This technology allows for more even cooking and better texture in reheated food.
FAQs
FAQ 1: How do microwaves cook food?
Microwaves cook food by emitting electromagnetic waves that cause water molecules in the food to vibrate, producing heat.
FAQ 2: Are microwaves safe to use?
Yes, microwaves are safe to use when operated according to the manufacturer’s instructions and using microwave-safe containers.
FAQ 3: Can microwaves cause cancer?
There is no scientific evidence to suggest that microwaves cause cancer. They use non-ionizing radiation, which does not have enough energy to damage DNA.
FAQ 4: Do microwaves destroy nutrients in food?
Microwaves can actually preserve more nutrients compared to other cooking methods, as they cook food quickly and with less water.
FAQ 5: What materials are safe to use in a microwave?
Microwave-safe materials include glass, ceramic, and certain plastics. Avoid using metal or aluminum foil.
Conclusion
Microwave ovens are a marvel of modern technology, offering a quick and efficient way to cook and reheat food. Understanding how they work, their history, and practical tips for using them can enhance your cooking experience. While common misconceptions exist, scientific evidence supports the safety and efficiency of microwaves. With advancements in technology, microwaves continue to evolve, providing even more versatility in the kitchen.
Relevant Data Table
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Frequency | 2.45 GHz |
| Magnetron | Generates microwaves by converting electrical energy |
| Waveguide | Directs microwaves from magnetron to cooking chamber |
| Turntable | Rotates food for even cooking |
| Convection Microwave | Combines microwave and convection cooking |
| Inverter Microwave | Provides continuous power for even cooking |