Understanding Microwave Radiation
The kitchen is a hub of modern technology, and one of its mainstays is the microwave oven. People often wonder about the safety of this ubiquitous appliance, specifically whether it emits radiation. This question is not just rooted in curiosity but also in concerns about health and well-being. To understand the nature of microwaves and their impact, we need to delve into their workings, the science behind the radiation they emit, and the safety measures in place.
Microwave ovens have revolutionized cooking since their invention in the mid-20th century. They work by emitting microwave radiation, a form of non-ionizing radiation, to heat food. This radiation causes water molecules in the food to vibrate, producing heat that cooks the food quickly and efficiently. But does this process pose any risk to humans? Let’s explore the details.
The Basics of Microwave Ovens
How Microwaves Work
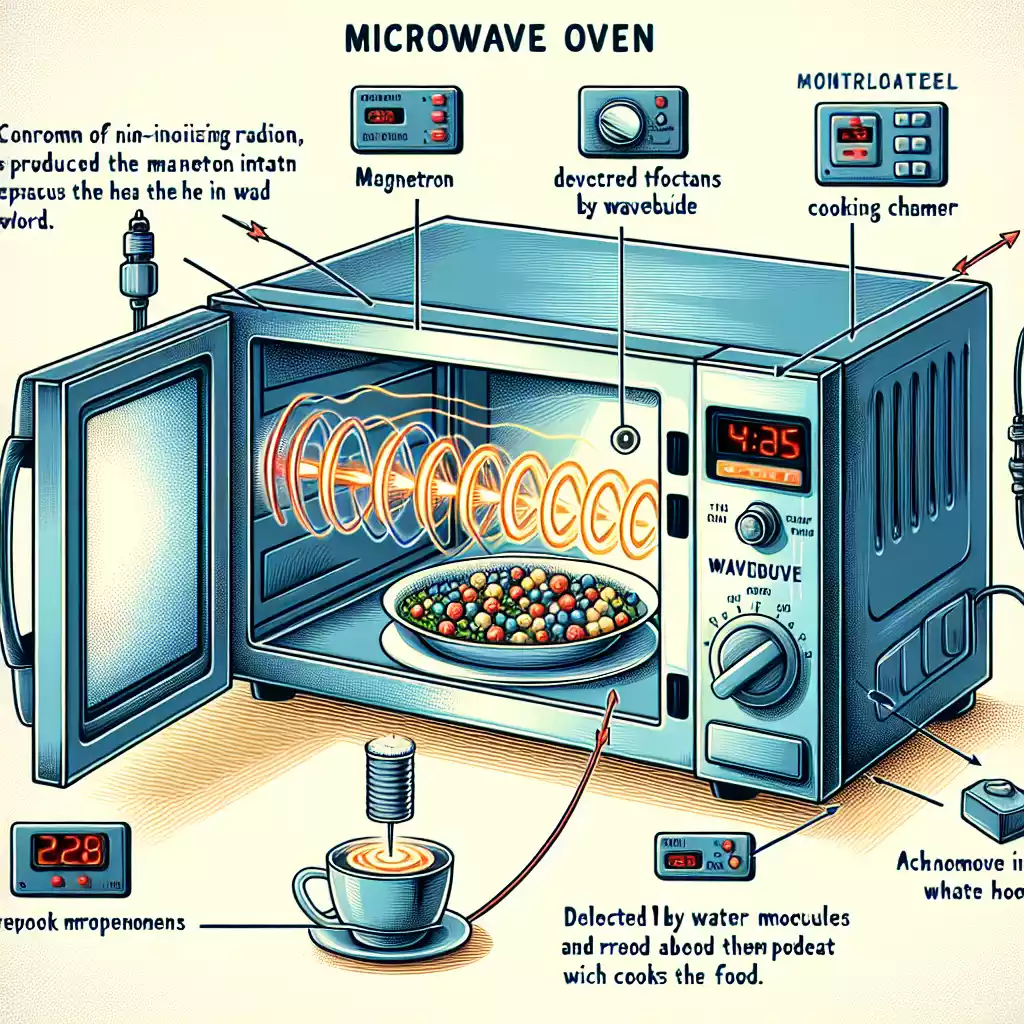
Microwaves use electromagnetic waves to heat food. These waves are generated by a component called the magnetron, which converts electrical energy into microwave radiation. The microwaves penetrate the food, causing water molecules to vibrate rapidly, generating heat through friction. This method cooks food from the inside out, unlike traditional ovens that heat from the outside in.
Components of a Microwave Oven
• Magnetron: The heart of the microwave, generating the microwaves.
• Waveguide: Channels the microwaves from the magnetron to the cooking chamber.
• Turntable: Ensures even cooking by rotating the food.
• Control Panel: Allows users to set cooking times and power levels.
The Science Behind Microwave Radiation
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Microwave radiation is part of the electromagnetic spectrum, which includes a range of wavelengths from radio waves to gamma rays. Microwaves fall between radio waves and infrared radiation, with wavelengths ranging from one meter to one millimeter.
Microwave Frequencies and Wavelengths
Microwaves used in ovens typically operate at a frequency of 2.45 gigahertz (GHz). This frequency is ideal for heating water molecules without causing ionization, which can be harmful.
Types of Radiation
Ionizing vs. Non-Ionizing Radiation
• Ionizing Radiation: High-energy radiation that can remove tightly bound electrons from atoms, potentially causing cell damage. Examples include X-rays and gamma rays.
• Non-Ionizing Radiation: Lower-energy radiation that does not have enough energy to ionize atoms. Microwaves fall into this category, making them generally safer.
Where Microwave Radiation Falls
Microwave radiation is non-ionizing, meaning it lacks the energy to alter the chemical structure of substances it interacts with. This characteristic makes it less dangerous compared to ionizing radiation.
Health Concerns and Safety
Common Myths About Microwave Radiation
• Myth: Microwaves cause cancer.
• Fact: There is no scientific evidence linking microwave use to cancer.
• Myth: Microwaves make food radioactive.
• Fact: Microwaves do not have enough energy to make food radioactive.
Scientific Studies on Microwave Safety
Numerous studies have investigated the safety of microwave ovens. Research consistently shows that when used according to manufacturer guidelines, microwaves are safe for daily use. Proper maintenance and adherence to safety instructions minimize any potential risks.
Regulatory Standards
International Guidelines
Organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) set strict guidelines for microwave oven safety. These guidelines ensure that microwaves operate within safe limits of radiation emission.
Compliance and Testing Procedures
Manufacturers must comply with safety standards and undergo rigorous testing. This includes ensuring that microwave leakage levels are well below the limits set by regulatory bodies.
Practical Tips for Microwave Use
Safe Practices in the Kitchen
• Use microwave-safe containers: Avoid metal and certain plastics.
• Do not operate an empty microwave: This can damage the appliance.
• Check for door seal integrity: Ensure the door closes properly to prevent radiation leakage.
Maintenance and Inspection
Regularly inspect your microwave for signs of wear and tear. Clean the interior and exterior to maintain optimal performance. If you notice any issues, consult the user manual or contact a professional for repairs.
Innovations in Microwave Technology
Advances in Microwave Design
Modern microwaves come with features like sensor cooking, inverter technology, and convection capabilities. These advancements improve cooking efficiency and user convenience.
Future Trends in Microwave Ovens
The future of microwave technology includes integration with smart home systems, energy efficiency improvements, and enhanced safety features. These innovations aim to make microwave ovens even more user-friendly and safe.
Relevant Data Table: Microwave Radiation Facts
| Fact | Details |
|---|---|
| Frequency | 2.45 GHz |
| Type of Radiation | Non-Ionizing |
| Regulatory Bodies | WHO, FDA |
| Common Myths | Cancer, Radioactive Food |
| Safety Tips | Use Microwave-Safe Containers, Regular Maintenance |
FAQs
FAQ 1: What is microwave radiation?
Microwave radiation is a form of non-ionizing radiation used in microwave ovens to heat food. It falls within the electromagnetic spectrum and operates at a frequency of 2.45 GHz.
FAQ 2: Is microwave radiation harmful to humans?
When used according to manufacturer guidelines, microwave radiation is not harmful. It is non-ionizing, meaning it lacks the energy to cause cellular damage.
FAQ 3: How can I ensure my microwave is safe to use?
Ensure the door seal is intact, use microwave-safe containers, and avoid operating an empty microwave. Regular maintenance and inspections are also crucial.
FAQ 4: What are the benefits of using a microwave oven?
Microwave ovens offer quick and efficient cooking, preserve nutrients better than some other cooking methods, and are convenient for reheating and defrosting.
FAQ 5: Are there foods that should not be microwaved?
Yes, avoid microwaving eggs in their shell, certain plastics, and metals. Also, be cautious with foods that can overheat and cause burns, like water and certain oils.
Conclusion
Understanding the nature of microwave radiation and its safety is essential for making informed decisions about using this common kitchen appliance. Microwave ovens use non-ionizing radiation to heat food efficiently and safely when used correctly. By following safety guidelines and keeping your microwave well-maintained, you can enjoy its benefits without worry.